Contents
- Introduction to Postpartum Hemorrhage
- Risk Factors
- Types
- Early PPH
- Late PPH
- Causes
- Early PPH
- Placental problems
- Uterine atony
- Other causes
- Late postpartum hemorrhage
- Management of PPH
- Homoeopathic treatment of PPH
- Short Repertory of PPH
- Bibliography
Mrs. Ya***da, 23 years, primigravida, primipara, met with PPH, about 3 hours after normal vaginal delivery (NVD). The blood was flowing in gushes, like a hydrant. During the way from maternity ward to operation theatre, she went into hypoaemic, hypovolemic, hypoxic shock and almost collapsed with staring and fixed eyes, pallor, cold body, cold perspiration and unconsciousness.
On examination, her pulse was almost imperceptible due to very low volume, BP 20/00 mm Hg, SpO2 06, HR 110/m, RR 30/m and rigors.
Intensive care unit evoked and started combatting with the crises. Central line oxygen perfusion, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, intravenous fluids with Ringer’s lactate and DNS (5% Dextrose with normal saline), Dopamine infusion, Noradrenaline infusion and Hydrocortisone injection were immediately administered. Oxytocin, Misoprostol, Methergine, Tranexamic acid (TXA) and Ethamsylate injections were immediately given.
But, alas! No result was there. It was the time to call me to do something with Homoeopathy. In OT, the entire scene was displayed clearly, but the worst failure was only observed by a Homoeopath. That was the Causa occasionalis. Until and unless, the bleeding is not stopped, what could be done?
I advised to first clip all the bleeders in womb with artery forceps and to start compatible blood transfusion in the form of Packed RBCs.
Till then, I got my memory back and recollected the line from Calvin Knerr’s repertory- ‘Repertory of Hering’s Guiding Symptoms of our Materia Medica- ‘General, Faintness, Hemorrhage, Postpartum, from.
A drop of IPECACUNHA 200 was administered into her Oxygen mask and the miracle begins within 5 seconds. The BP shoots up to the 180/135 mm Hg, SpO2 92 %, Pulse bounding, full, HR 125/m, RR 21/m, shrieking and moaning due to pain in uterus started.
The doses of Dopamine and Noradrenaline infusions were reduced from 10 units per minute to 4 UPM. Now the BP settled to 135/85 and the condition became under control.
As soon as these vitals got revived, the bleeders were quickly sutured with catgut and packing of womb was done with 5% Hamamelis Q and Betadine solution.
China 200 was administered 3 hours after operation and maintained at the rate of one dose every 6 hours.
After 12 hours, the patient restored her health and started taking her meals and discharged two days after the incidence.
Here, we can easily see the importance of removal of causa occasionalis and role of Homoeopathy in emergencies, where well administered modern medicines fail to act.
Introduction to Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is the rapid or slow loss of 500 mL of blood after delivery. Severe PPH is when there is blood loss of 1000 ml within the same time frame. This complication occurs in 5%–10% of term deliveries. Further complications of PPH include shock, anemia, and infection.
Some definitions have included signs and symptoms of hemodynamic instability-
• Hypotension
• Tachycardia
• Altered mental status
Risk Factors
PPH can happen to anybody. There are risk factors for PPH such as-
• Having a previous PPH
• Multiple pregnancy
• Anemia
• A large baby
• Placenta abnormalities
• Prolonged labor
• Chorio-amnionitis
• Placental abruption and
• A cesarean section
Types
Early PPH
It occurs within 24 h of birth.
Late PPH
It may occur 24 h to 4 weeks after birth.
Causes
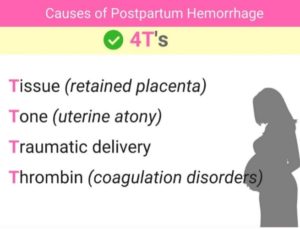
There are the “Four Ts” of PPH –
• Tone
• Trauma
• Tissue
• Thrombin
Early PPH
It may be caused by-
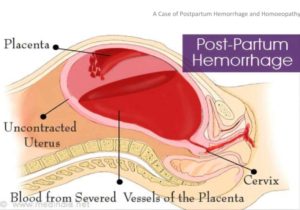
Placental problems
• Abruptio placentae
• Placenta previa
• Incomplete placental separation
Uterine atony
• Anesthesia
• Marked pre-delivery uterine distention
• Abnormal labor
• Prolonged or excessive oxytocin administration
Other causes
• Over-distended urinary bladder
• Lacerations of the birth canal
• Rupture of the uterus
• Blood dyscrasias like hypofibrogenemia
• Mismanagement of the third stage of labor
Late postpartum hemorrhage
It is due to retained products of conception.
Management of PPH
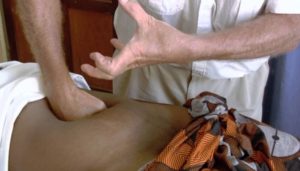
Post-partum hemorrhage is treated rapidly by four interventions-
• Uterine massage
• Uterotonics- Misoprostol by intrauterine route
• IV fluids (crystalloids) and
• Trranexamic acid
If not controlled, these interventions are also include-
• Aorta compression
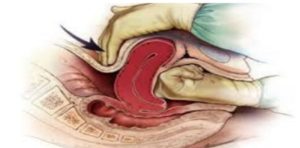
• Bimanual uterine compression
• Uterine balloon tamponade (UBT)
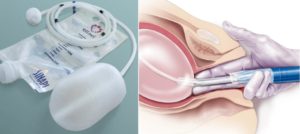
• Non-Pneumatic Anti-Shock Garment (NASG)

• Oxytocin
• Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
• Compression Sutures- Uterine compression sutures are a medical procedure used to assist in the treatment of PPH, and specifically with the goal of avoiding a hysterectomy, which can be a last-resort treatment for PPH.
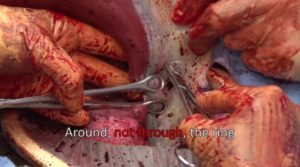
• Suturing Internal Iliac Artery (IIA) – complete or partial, to reduce the volume of blood flow.
Homoeopathic treatment of PPH
No person other than Kent has written about the application and limitations of Homoeopathy in PPH. “When I say haemorrhages, I do not mean those from cut arteries, I do not mean haemorrhages where surgery must come in; I mean such as uterine haemorrhages, haemorrhages from the kidneys, from the bowels, from the stomach, from the lungs. You must know your remedies in haemorrhages; if you do not, you will be forced to use mechanical means; but the homeopathist who is well instructed is able to do without them. In the severest form of uterine hemorrhages, the homeopathic physician is able to do without mechanical means, except when mechanical means are causing the haemorrhage. This does not relate to hourglass contractions, it does not relate to conditions when the after birth is retained, or when the uterus has a foreign substance in it, because under such circumstances manipulation is necessary.
A distinction must be made. But when we have simply the pure dynamic element to consider, simply and purely a relaxed surface that is bleeding, the remedy is the only thing that will do the work properly. When the uterus is continuously oozing, but every little while the flow increases to a gush, and with every little gush of bright red blood the woman thinks she is going to faint, or there is gasping, and the quantity of the flow is not sufficient to account for such prostration, nausea, syncope, pallor, Ipecac. is the remedy.
When with the gushing of bright red blood there is an overwhelming fear of death, Aconite. If your patient while going through the confinement has had a hot head, an uncontrollable thirst for ice cold water, and after the confinement, everything has gone on in an orderly way, and the placenta has been delivered, and although you have no reason to expect such haemorrhage it comes on, Phosphorus will nearly always be the remedy.
In those withered women, lean and slender, who are always suffering from the heat, who want the covers off and want to be cool, who have had a tendency to ooze blood from the uterus, and now have a haemorrhage that is alarming either with clots, or only an oozing of dark liquid blood, you can hardly do without Secale. A single dose of any one of these medicines on the tongue will check a haemorrhage more quickly than large doses of strong medicine. The haemorrhage will be checked so speedily that in your earlier experiences you will be surprised. You will wonder if it is not possible that it stopped itself. In copious menstruation Ipecac. is often indicated When the woman has taken cold, or has a shock. In cases where she is not especially subject to copious uterine flow at the menstrual period, she is naturally alarmed, for it is something she has never bad before, and the flow is likely to continue for many days, attended with this weakness. All her power seems to go with a little gush of blood. Ipecac. will cure and end the menstrual flow normally. A fortunate thing in nature is the tendency to check haemorrhage, which is always good.
There are a large number of medicines that control haemorrhage, and these you must keep at your finger’s ends. They belong to emergencies. You must know the remedies that correspond to violent symptoms and violent attacks. Ipecac. is full of hemorrhage. Vomiting of great clots of blood, continuous vomiting of blood in connection with ulceration. In persons who are subject to violent attacks of bleeding, who bleed easily, who have a haemorrhagic tendency, Ipecac. will control temporarily the haemorrhage when the symptoms agree.”
Short Repertory of PPH
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – after: (33) Acet-ac. am-m. aml-ns. Arn. ars. bell. bell-p. cann-s. caul. cham. Chin. Cinnm. Croc. crot-h. cycl. erig. ferr. ger. Ham. hyos. ign. ip. kali-c. mill. nit-ac. nux-v. Plat. puls. sabin. sec. thlas. tril-p. ust.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – after – eight days: (1) Sabin.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – after – one week: (1) Kali-c.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – after – some days: (1) CINNM.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – after – two weeks: (1) Ust.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – during and after: (54) Acet-ac. acon. adren. alet. alum. apis Arn. Bell. bry. Cann-i. cann-s. carb-v. caul. Cham. Chin. Cinnm. cocc. coff. Croc. crot-h. ERIG. Ferr. Gels. ger. HAM. Hydr. Hyos. IP. kali-c. kalm. kreos. lach. lyc. merc. mill. nit-ac. nux-m. nux-v. op. ph-ac. Phos. Plat. plb. psor. puls. Rhus-t. SABIN. SEC. senec. sep. Thlas. thyr. tril-p. Ust.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – gushing: (2) bell. Ip.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – inertia uteri, with: (5) am-m. caul. puls. sec. Ust.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – motion; slightest: (1) CROC.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – offensive: (1) Nit-ac.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – prevents hemorrhagia: (1) Arn.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – profuse: (4) APIS Ip. Plat. Sabin.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – delivery – putrid: (1) Ust.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – displacement of uterus; from: (1) tril-p.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – dysuria; with: (2) erig. mit.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – exertion agg.; after: (13) AMBR. Aur. Bov. CALC. cinnm. Croc. ERIG. Helon. mill. Nit-ac. rhus-t. Sabin. Tril-p.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – faintness; with: (6) apis chin. ferr. Ip. Kreos. TRIL-P.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – false step; after: (1) cinnm.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – gushing: (18) Bell. Borx. bov. Cham. chin. Cinnm. Croc. Erig. Ham. IP. Lac-c. Mill. PHOS. Puls. SABIN. Sec. tril-p. Ust.
FEMALE GENITALIA/SEX – METRORRHAGIA – hot – delivery; during: (1) ip.
Bibliography
- 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin) and Dopamine > Use of Ergot Alkaloids in Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13e… hemorrhage. …
- Emergency Delivery > POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE Book: Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 9e … TABLE 101-7 Risk Factors for Postpartum Hemorrhage Primiparity or grand multiparity Previous postpartum hemorrhage Preeclampsia Prior cesarean section Placenta previa ..
- Gynecology > Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: Schwartz’s Principles of Surgery, 11e … Postpartum hemorrhage is an obstetrical emergency that can follow either vaginal or cesarean delivery. Hemorrhage is usually caused by uterine atony, trauma to the genital tract, or rarely, coagulation disorders. Hemorrhage may also be caused by abnormal placentation (also called morbidly…
- Introduction to Endocrinology: The Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis > Prevention and Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13e…. The infusion rate then is reduced to 1–2 mU/min until the mother is ready for transfer to the postpartum unit. …
- Obstetric and Gynecologic Emergencies and Sexual Assault > POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE Book: CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Emergency Medicine, 8e
- Obstetric Anesthesia > POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE Book: Morgan & Mikhail’s Clinical Anesthesiology, 6e… Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality in developing countries, and it is diagnosed when postpartum blood loss exceeds 500 mL. Up to 4% of parturients may experience postpartum hemorrhage, which is often associated with a prolonged third stage of labor, preeclampsia…
- Obstetrical Hemorrhage > Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: Williams Obstetrics, 25e… In most cases, the source of postpartum hemorrhage can and should be determined. Frequent causes are uterine atony with placental site bleeding, genital tract trauma, or both. Postpartum hemorrhage is usually obvious. Important exceptions are unrecognized intrauterine and intravaginal blood…
- Obstetrics/Gynecology > Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: Improvised Medicine: Providing Care in Extreme Environments, 2e… Hemorrhage is the underlying cause of >25% of maternal deaths in the developing world. Blood loss occurs rapidly, because the gravid uterine blood flow is 600 to 900 mL/min at term. With uterine atony, the woman loses blood at the rate of > 500 mL/min. Early postpartum hemorrhage is seen…
- Radar Opus
- Postpartum Hemorrhage & the Abnormal Puerperium > B. Management of Delayed Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Obstetrics & Gynecology, 12e… Delayed postpartum hemorrhage (bleeding ≥ 2 weeks after delivery) is almost always due to subinvolution of the placental bed or retained placental fragments. Involution of the placental site is normally delayed when compared..
- Special Population: Pregnant Women > POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE Book: CURRENT Practice Guidelines in Primary Care 2019
- The Puerperium > Late Postpartum Hemorrhage Book: Williams Obstetrics, 25e… Secondary postpartum hemorrhage is defined as bleeding 24 hours to 12 weeks after delivery. Clinically worrisome uterine hemorrhage develops within 1 to 2 weeks in perhaps 1 percent of women. Such bleeding most often is the result of abnormal involution of the placental site. It occasionally…
- Encyclopedia Homoeopathica
- Radar 10
About Author
Dr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma M.D. (Homoeopathy) Homoeo Cure & Research Institute, India


