ORIGIN OF WORD
The word dandruff is derived from dand (origin unknown) and hurf, meaning “scab”. This is probably linked to the Old Norse word hrufa, meaning “scab”. The Old High German word hruf means “scurf”.
DEFINITION
Dandruff is the presence, in varying amounts, of white or gray scales in the hair of the scalp, due to excessive or normal branny exfoliation of the epidermis as a consequence of the common, asymptomatic, fluffy, clinical expression of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp and has been referred to as Pityriasis sicca, scurf or Pityriasis simplex capillitii.

PATHOGENESIS
The disease is characterized by scaling (Psora/ Sycosis) on an erythematous base (Psora). The scale often has a yellow, greasy appearance. Itching may be severe (Psora). Dandruff causes flakes of skin to appear (Psora/ Sycosis). When the skin cells on our scalp are renewed the old ones are pushed to the surface and out of the scalp. With dandruff, the renewal of skin is faster; more dead skin is shed, making the dandruff more noticeable.
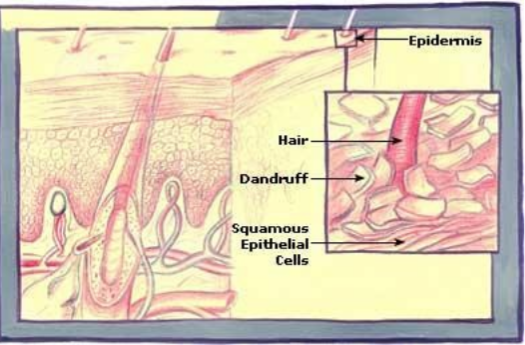
TYPES
Dandruff can be chronic or the result of certain triggers (Causa occasionalis). Erythema paranasale, more common in young women than men, may be part of this disease spectrum.
There are three main types of dandruff.
OIL-RELATED DANDRUFF
It occurs from bad hygiene practices. Sebum, if left, can combine with dead skin and dirt to form dandruff.
YEAST-RELATED DANDRUFF
It is formed due to the presence of a fungus – Malassezia furfur; present on most everyone’s scalps without causing problems with dandruff (Pseudopsora). Whenever excess skin oil is present on the scalp (Psora/ Sycosis), the oil provides enough food for the fungus to grow out of control. It causes the skin to become irritated and form additional skin cells on the scalp.
DISEASE-RELATED DANDRUFF
It forms as a secondary side effect of scalp conditions, e.g. psoriasis (Psora/ Sycosis/ Syphilis). As the additional skin cells shed, they can combine with sebum oil into dandruff. In eczema (Psora/ Pseudopsora), dry flaky skin on the scalp can fund to dandruff formation.
CAUSES
Its aetiology is unknown. Involvement of sebum is supported by clinical observations of people with Parkinson disease, who typically show increased sebum production secondary to dopamine deficiency and have a markedly increased incidence of seborrhoeic dermatitis.
Dandruff can occur if the scalp is frequently exposed to extreme temperatures. Excessive flaking may be caused by an underlying illness or condition, such as psoriasis, Malassezia furfur infection, seborrheic dermatitis, or even head lice.
CLINICAL PICTURE
There are white flakes of skin on the scalp, and hair.
- Flakes may be oily looking
- Head may feel tight and itchy
- Head may feel tingly
- Head may feel sore
- Red, flaky, greasy patches of skin (adults, Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in adults)
- Crusting and scaling rash on scalp (babies with Seborrheic dermatitis, or cradle cap)
It classically involves regions of rich in of sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, forehead, especially the glabella, external auditory canal, retroauricular area, nasolabial folds, and the presternal area.
In infants, seborrheic dermatitis presents as cradle cap. Here it can also be part of Leiner disease, in which the condition is generalized and associated with diarrhea and failure to thrive.
A severe form of seborrheic dermatitis that is difficult to treat is seen in many HIV– infected individuals with low CD4 counts.
TREATMENT
Usually, dandruff does not require medical attention. However, sometimes the flaking and itching that appears like dandruff is really a medical condition, such as seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, fungal infections of the scalp, or eczema. Treatment depends on root cause.
DANDRUFF AND HOMOEOPATHY
agar. all-s. aloe alum. AM-M. anac. ARS. ars-br. asim. aur. bad. BAR-C. bran. bros-au. BRY. bufo CALC. calc-p. CALC-S. CANTH. CARBN-S. carc. cean. chinin-s. choc. cic. citl-g. coch. CROT-H. DULC. dys. fl-ac. germ-met. granit-m. GRAPH. grat. hep. hera. HYDR. hydrog. ictod. iod. jab. KALI-BR. KALI-C. kali-chl. kali-m. kali-p. KALI-S. kola kreos. lac-. Lach. led. LYC. MAG-C. mag-p. maland. MED. merc. MEZ. NAT-M. nicc. OLND. oncor-. par. petr. PHOS. porc-m. positr. propr. PSOR. quill. rad-br. Rhus-t. rosm. ruta sanic. saroth. SEP. sil. stann. STAPH. sul-i. SULPH. term-c. THUJ. tritic-vg. tub. uran-met. URT-U. vanil.
REPERTORY OF DANDRUFF
Brows – dandruff sanic. Dandruff – itching med. Dandruff – scaly, profuse sanic.
Dandruff – white ars. kali-m. mez. Nat-m. Thuj. Dandruff – yellow calc. Kali-s.
Dandruff ars. canth. Graph. lyc. nat-m. Phos. staph. sulph. thuj.
Eyebrows – lashes – dandruff sanic.
Eyes – ERUPTIONS, eyes – eyebrows, about the – dandruff sanic.
FACE – DANDRUFF – Eyebrows sanic. sulph.
FACE – DANDRUFF, beard chinin-s.
FACE – ERUPTIONS – dandruff, eyebrows sanic.
Generals – HAIR, general, head and body – falling, out, of hair – dandruff, due to am-m. kali-c. thuj.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – greasy skin, with maland. HEAD – DANDRUFF – horny kola
HEAD – DANDRUFF – itching MED.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – itching med. positr. propr. ruta
HEAD – DANDRUFF – Occiput nat-m. sep.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – scaly – profuse sanic.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – scaly sanic. term-c. HEAD
– DANDRUFF – scaly, profuse sanic.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – skin, with greasy maland.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – white alum. ars. choc. KALI-M. kola MEZ. NAT-M. olnd. PHOS. THUJ.
HEAD – DANDRUFF – yellow calc. KALI-S.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – copious, falls out in clouds Phos.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – enormous canth. kali-s.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – headache, with, in pregnancy calc.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – herpetic – circles like ringworm, in sep.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – herpetic graph. nat-m.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – scaly – hair comes out, skin peels off with itching and smarting staph.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – scaly canth. Kali-s. THUJ.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – smells, badly Lyc. Psor.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – weather, worse in change of Dulc.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – white – flakes, in, with itching kali-m.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – white – white and dry mez. nat-m.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – white alum. choc. Kali-chl. kali-m. Mez. NAT-M. Phos. THUJ.
Head – DANDRUFF, scalp – yellow KALI-S.
HEAD – DRYNESS – hair – falling, and, with dandruff KALI-C.
HEAD – External – dandruff – occiput, on nat-m. sep.
HEAD – External – dandruff alum. Ars. GRAPH. kali-c. Olnd. phos. stann. sulph.
HEAD – FALLING out, hair, alopecia – dandruff, from am-m. thuj.
HEAD – HAIR – affections of – falling out, alopecia – dandruff, due to am-m. thuj.
HEAD – Scalp – Dandruff am-m. Ars. Bar-c. bran. bry. fl-ac. Graph. hep. hera. iod. Kali-s. lyc. nat-m. phos. sanic. Sep. sil. sul-i. sulph. thuj.
Pregnancy – HEADACHES, during pregnancy – dandruff, with Calc.
Bibliography
Seborrhea Dermatology > Chapter 22. Seborrheic Dermatitis
Antiseborrhea Agents Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 12e> Chapter 61 . Dermatologic Pharmacology
Seborrheic Dermatitis Harrison’s Online > Chapter 52. Eczema, Psoriasis, Cutaneous Infections, Acne, and Other Common Skin Disorders > Eczema and Dermatitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine > Chapter 134. Rashes in Infants and Children > Common Neonatal Rashes
Dandruff CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Pediatrics > Chapter 14. Skin > Common Skin Diseases in Infants, Children, & Adolescents > Dermatitis (Eczema)
Seborrheic dermatitis has both infantile and adult forms. The infantile form is called “… Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine > Chapter 246. Disorders of the Face and Scalp > Seborrheic Dermatitis
Figure 144-5. Cradle cap in an infant that also has atopic dermatitis. (Courtesy of Richard P…. The Color Atlas of Family Medicine > Chapter 144. Seborrheic Dermatitis > Diagnosis > Clinical Features
Figure 144-6. Mild seborrheic dermatitis with subtle flaking around the eyebrows of a 2-month-old… The Color Atlas of Family Medicine > Chapter 144. Seborrheic Dermatitis > Diagnosis > Clinical Features
Radar 10
Encyclopedia Homoeopathica
About Author
© Dr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma
M.D.(Homoeopathy)
Dr. Reena Rawat B.H.M.S.
Dr. Nancy Rastogi B.P.T., M.I.A.P.
Homoeo Cure & Research Centre P. Ltd., India

